Processing Equipment/Measuring Equipment
Processing Equipment

Peripheral Blade Peripheral edge grinders

Peripheral Blade Peripheral edge grinders
Peripheral Blade Peripheral edge grinders grind the outer circumference of a tool by rotating the grinding wheel and applying it perpendicularly to the tool's axis of rotation. Grinding wheels are made of abrasive material containing grit, ranging in size from tens of centimeters to several meters in diameter. The grinding wheel is carved into a shape suitable for the grinding process, and rotates to cut the rear cutting edge.

Rotary grinders

Rotary grinders
Rotary grinders are used by fixing the workpiece and then moving the grinding wheel against the workpiece while simultaneously rotating the workpiece and grinding wheel. Grinding wheels are rotating tools and come in a variety of diameters, shapes and abrasive materials. In addition, there are two types of workpieces, one for internal grinding and the other for external grinding.
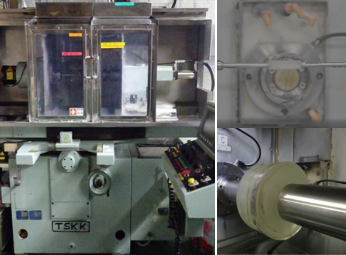
Cylindrical grinding machines

Cylindrical grinding machines
Cylindrical grinding machines can grind workpieces with large diameters and lengths. The workpiece is rotated by the workhead mounted on the grinder, and the grinding wheel is moved by a slide mounted on the wheelhead as it grinds the workpiece. Grinding wheels of various diameters, widths, materials and grits are selected according to the material and shape of the workpiece.

Wire saws

Wire saws
Wire saws are used to cut a wide variety of materials, including metals, non-metals and composites.
It is especially useful for cutting hard, brittle materials and large, thick materials. In addition, the wire saw generates less heat and vibration, reducing the possibility of distortion and deformation of the material after processing, enabling high-precision processing.

Chamfering machines

Chamfering machines
We also have various types of chamfering machines, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic equipment. Manual chamfering machines allow the operator to manually shave edges.
With semi-automatic chamfers, you simply set the edge and the machine will chamfer it automatically. Fully automatic chamfering machines help to enhance productivity because the entire line, including conveyors, is automated.
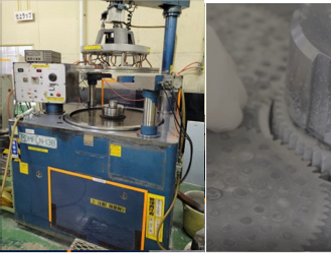
Lapping machine

Lapping machine
A lapping machine attaches the material to be polished to a special carrier and places it on the lapping surface plate. The carrier is sandwiched between the upper and lower lapping plates and the surface of the material is polished as the plates and carrier rotate. Lapping machines are suitable for fine machining due to their high-precision flatness and surface roughness control.
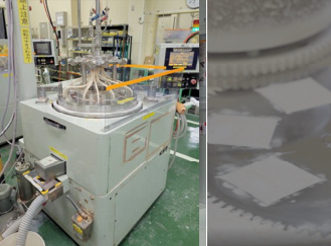
Polishing Machines

Polishing Machines
Polishers place the object to be polished, along with an abrasive, on a rotating polishing plate and the plate rotates while the special carrier moves to polish the workpiece.
Abrasives are typically diamond abrasives, silicon carbide, or other compounds, and polishing is performed with a jet of slurry.

Precision cleaners

Precision cleaners
Precision cleaners use water, organic solvents, alcohols, acids, and alkalis to remove oil and dirt particles from part surfaces. Typically, a combination of high pressure spraying, ultrasonic, vibration and time shot methods are used to remove dirt that has penetrated into microscopic holes and crevices.
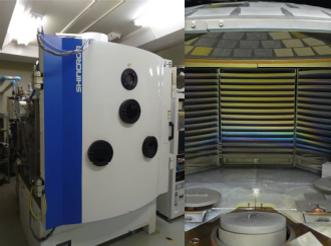
Vacuum evaporators

Vacuum evaporators
Vacuum evaporators are designed to allow evaporation in a vacuum. In a vacuum, where the mean free path of gas molecules is longer, collisions between a vaporized substance and gas molecules decrease.
This allows evaporated molecules to reach the surface and form a more uniform thin film.
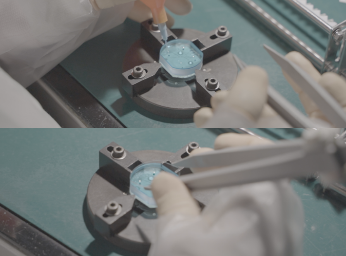
UV bonding

UV bonding
In UV bonding, a UV adhesive is applied to the surface to be bonded and is cured by ultraviolet irradiation.
The use of ultraviolet irradiation equipment allows a large number of parts to be bonded at once, making it suitable for automation. In addition, the adhesive is transparent and aesthetically pleasing after curing, making it suitable for high design quality products.
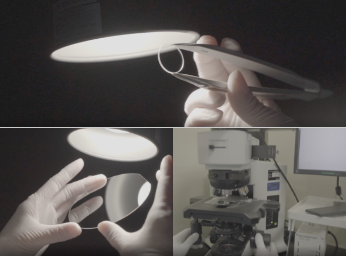
Inspection

Inspection
Inspection To measure the turbidity of an optical substrate, the substrate to be measured is sampled and measured with a turbidimeter. The extreme transparency of the optical substrates allows measurement of even the tiniest turbidity. In addition, the dependence of turbidity on the surface condition and shape of the optical substrate requires the operator to be aware of the surface condition and shape of the substrate being measured.
Measuring Equipment

Spectrophotometer

Spectrophotometer
We offer a variety of spectrophotometers in fixed and variable wavelengths. Variable wavelength spectrophotometers, use a spectrometer to spectrally split the light emitted from the light source, and the wavelength of the light irradiated to the sample can be varied. A fixed wavelength spectrophotometer emits light from a light source at a fixed wavelength. Variable wavelength spectrophotometers are suitable for quantitative analysis due to their broad wavelength range and the absorbance of the sample can be measured at multiple wavelengths. On the other hand, a fixed wavelength spectrophotometer is suitable for qualitative analysis because it can measure at different wavelengths.

Spectrophotometer

Spectrophotometer
We offer a variety of spectrophotometers in fixed and variable wavelengths. Variable wavelength spectrophotometers, use a spectrometer to spectrally split the light emitted from the light source, and the wavelength of the light irradiated to the sample can be varied. A fixed wavelength spectrophotometer emits light from a light source at a fixed wavelength. Variable wavelength spectrophotometers are suitable for quantitative analysis due to their broad wavelength range and the absorbance of the sample can be measured at multiple wavelengths. On the other hand, a fixed wavelength spectrophotometer is suitable for qualitative analysis because it can measure at different wavelengths.

Lens reflectometer

Lens reflectometer
A lens reflectometer is a measuring instrument used to study the optical properties of the surface of a material. This instrument shines light onto the surface of a sample, captures the reflected light with a lens, and measures it with an inspection machine to evaluate the sample's surface condition, film thickness, refractive index, etc.

High-resistivity meter

High-resistivity meter
A high-resistivity meter is a measuring instrument used to determine the resistivity of a material. It measures the resistivity of a sample by applying DC power to the sample and measuring the flowing current and applied voltage.

Contact angle meter

Contact angle meter
A contact angle meter is an instrument used to measure the surface tension or interfacial tension of a material. By dropping a liquid on the surface of a sample and measuring its contact angle, the contact angle meter can evaluate the hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity of the surface, surface energy, and the effect of surface treatment.

Turbidity Meter (HAZE meter)

Turbidity Meter (HAZE meter)
To measure the turbidity of an optical substrate, the substrate to be measured is sampled and measured with a turbidimeter.
The extreme transparency of the optical substrates allows measurement of even the tiniest turbidity.
In addition, the dependence of the turbidity on the surface condition and shape of the optical substrate requires the operator to pay attention to the surface condition and shape of the substrate being measured.

Laser displacement meter

Laser displacement meter
A laser displacement meter is a non-contact instrument used to measure minute displacements in an object. The laser displacement meter can measure the minute displacements of an object by irradiating a laser beam onto the object and capturing the reflected light with a light receiving element.

Oscilloscope

Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a measuring instrument used to observe the waveform of electrical signals, usually abbreviated as "oscillo." It can measure the amplitude, frequency, phase, etc. of a waveform, and can also detect signal distortion, noise etc. Oscilloscopes have a wide range of applications in fields such as electrical engineering and physics.

A laser interferometer

A laser interferometer
A laser interferometer measures a tiny displacement by measuring an interference fringe. This allows for extremely accurate measurements. It is widely used in fields such as precision machining, testing, and experiments. For example, it is used for measurement and evaluation of mechanical parts, measurement of optical elements, measurement of elastic modulus of materials, deformation analysis, and vibration analysis.

A phase difference meter

A phase difference meter
A phase difference meter is an electrical circuit used to detect the phase difference between two signals.
It typically compares two input signals and detects the phase difference between them.
The meters are used in electronic circuits, including frequency synthesizers, phase matching circuits, and phase control circuits.

